Frequency versus Audible Frequency questions
Frequency:
Referred as Temporal frequency.
No of occurrence of a repeating event per unit time.
Relation between frequency and time:
frequency = 1/ time.
Units of Frequency:
Hertz.
Who named Hertz?
Heinrich Hertz.
What is previous name of Hertz?
One cycle per second.
Angular Frequency:
Rate of change of angular displacement.
Angular Displacement:
Angle of radians through which a point is rotated in specified axes.
Spatial Frequency:
Similar to temporal frequency.
But time axis is replaced by one or more spatial displacement.
Spatial Displacement:
Most commonly recognized form.
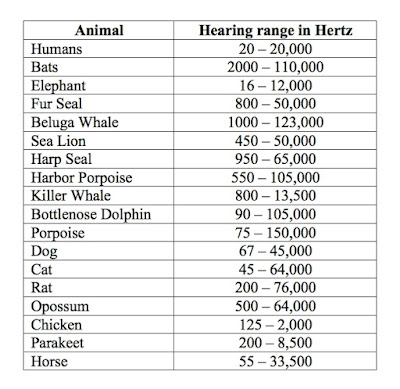
Audio Frequency:
Frequency audible to human.
Cutoff Frequency:
At which energy flowing through it is reduced rather than passing through.
Negative Frequency:
Forward travelling waves.
Positive Frequency:
Backward travelling waves.
Reason behind forward travelling and backward travelling:
If we have a equation that is of standard form with positive constant velocity but when we place it in graph it moves backward. Similarly with forward travelling.
Radio Frequency:
It is of electromagnetic waves that lie in the range of 3khz to 300 ghz.
Electromagnetic Waves:
Travel through vacuum.
Natural Frequency:
Tends to vibrate when somehow disturbed.
Interaction Frequency:
No of social interaction per unit time.
Social Interaction:
Social exchange between two or more groups.
Frequency changer:
Converts one AC signal of frequency to another AC signal frequency.
Application of Frequency changer:
Control speed of motor, pumps and fans.
Frequency domain:
Analysis of mathematical function with respect to frequency rather than time.
Frequency distribution:
Displays frequency of various outcomes in a sample.
Frequency band:
Specific range of frequencies in spectrum from very low frequencies to extremely high frequencies.
Spectrum:
Not limited to specific value but can vary without steps.
Frequency extender:
Allows high fidelity analogue audio to be sent over POTS telephone lines, without loss of higher audio frequency.
POTS:
Plain old telephone service.
Used in home.
High fidelity:
As same as original signal.
Frequency Grid:
Table of all central frequencies of channels allowed in communication system.
Frequency modulation:
Encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of wave.